
Home / EV Charging News / How Long Does An Electric Car Battery Last?
Electric Vehicles (EVs) are becoming the preferred transport choice for many American families. These vehicles are cheap, reliable, efficient, and good for the environment, but have you ever wondered how many years do EV batteries last? The battery replacement is one of the most expensive parts in an EV, which is why you should be entirely aware of its lifespan and other important information.
In this article, we will explain everything you need to know about EV batteries and answer the question of how long should an electric car battery last. Here we will explain the lifespan of batteries in cycles, miles driven, and years. We will also explain how they degrade and give you important tips to optimize the battery life of your EV.
EV batteries are made out of Lithium-Ion just like the batteries on your phone, after all, this is the highest energy density electrolyte available in mass production. There are a few variations considered among the Lithium-Ion electrolytes, the most popular compositions are Lithium-Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt-Oxide (NMC) and Lithium-Nickel-Cobalt-Aluminum Oxide (NCA).
Electric car battery life expectancy has reached its end when the traction battery pack can only retain 80% of its designed capacity. Manufacturers like Nissan, Chevy, and Tesla, cover most of their EVs for the EV battery life, going for 100,000 miles or up to 8 years.
After an electric car battery lifespan can retain only 80% of its capacity, it will degrade at a faster pace. However, even though an electric car battery has reached the end of its lifespan, it has been found that EV batteries can satisfy the needs of most EV drivers until they only hold 50% of their designed capacity.
Some studies show that an EV battery has truly reached the end of its lifespan after 200,000 miles of driving or around 12 years. At this point, you may need to exchange the EV battery, which ranges in cost from $3,000 up to more than $20,000.
Lithium-Ion EV batteries feature a limited number of charge and discharge cycles. Learning about the devices and external factors that consume your battery, allows you to reduce the pace at which it is discharged, therefore extending the electric vehicle battery life.
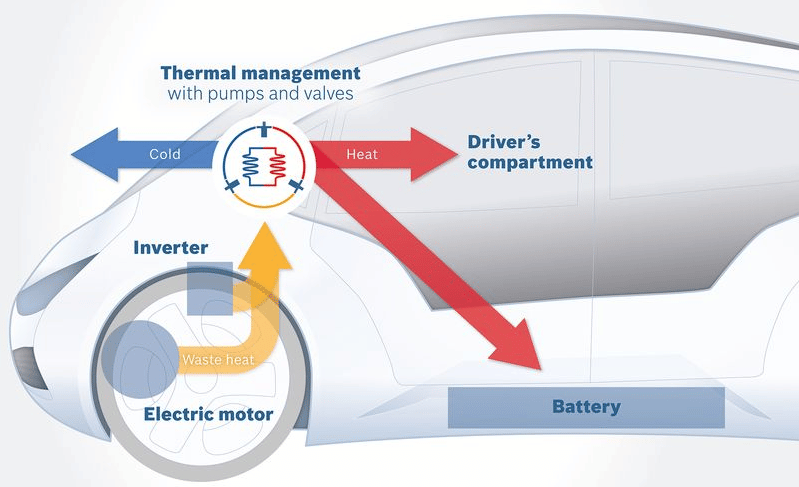
Figure 2: Battery THermal Management System
The Battery Thermal Management System (BTMS) or battery heating and cooling system, is a thermodynamic and heat transfer system that maintains ideal temperatures of 20ºC to 40ºC at the battery. This is a vital system for vehicle performance and battery life, since exposing batteries to extreme temperatures can rapidly drain their capacity, lower their performance, and reduce their lifespan.
The specific power consumption varies on the BTMS used for an EV. On ideal conditions, the BTMS consumes less than 1 kW, less than ideal temperatures make the BTMS consumption go up from 1 kW to 2 kW, while extreme cold temperatures require using a resistive heater that consumes more than 5 kW.
Aside from the primary vehicle systems like the Electric Engine that consumes 0.25 to 0.50 kWh/mile and the BTMS, there are secondary vehicle systems and external factors that drain your EV battery. Most of these consume a small amount of power but adding these up results in battery drainage that reduces the driving range of your EV.
To help you estimate and extend the average battery life of your electric car, we recommend learning the average scoring for secondary vehicle systems. This is the best way to keep tabs on devices that take a little power from your battery at a time. In the following sections, we dive into these secondary systems and explain how much power they demand from your vehicle.
The HVAC system or cabin heating and cooling system are one of the largest battery drainers. Some HVAC systems take from 3 – 4 kW to operate air conditioning, while EVs like the Tesla Model 3 consumes 4.8 kW to keep temperature cold, and consume up to 6.4 kW to start cooling the cabin.
The heating system demands 4.3 kW up to 8 kW to heat the cabin. It is estimated that the HVAC system consumes 5% up to 15% of your average EV battery life, being one of the largest battery drains. Only using the seat heater, demands around 500W or 0.5 kW from your battery.
The lighting system on an EV requires a small amount of power since it uses efficient technology that consumes less than 50 Wh. This is equivalent to reducing nearly 9 miles from the remaining driving range of the vehicle.
EVs are usually equipped with 200 W audio systems, but they consume on average 20 W, making them quite efficient. The problem comes with modern infotainment systems featuring several displays and high-capacity processors that consume around 350 W since they represent a higher challenge for the average EV battery life.
EVs come with USB chargers used to recharge smartphones (25 Wh), tablets (25 Wh), and other electronics. These chargers and other components like the windscreen wipers, demand a small toll from your electric car battery life cycle, consuming the equivalent of 30 ft. of driving range per charging hour.
Many EVs feature Anti-Lock Braking Systems (ABS), suspension compressors, and other components that aid the driving experience. These secondary driving components demand a small amount of energy of around 100 Wh, equivalent to 0.3 miles of your driving range per hour of drive.
However, it is important to consider the regenerative braking system. This system can reabsorb 10% to 25% of the energy spend while driving in urban locations.
Top speed and aerodynamic designs can also impact the performance and average life of an electric car battery. EVs like the Tesla Model 3 feature an aerodynamic coefficient drag (Cd) of 0.23, while the Lightyear One broke this record for EVs with a Cd lower than 0.20.
Aerodynamic drag makes EV engines consume around 9.5 kW at 70 mph, reducing the speed to 68 mph can impact battery life, reducing drag consumption down to 8.7 kW. This highlights the importance of aerodynamic Cd and top speed on the average life of an EV battery.
Increasing weight in an EV by considering the passengers and luggage can impact the electric car battery life. On average, increasing the weight of the EV by 1% increases electricity consumption by 1%. Meaning that every 40 – 50 pounds, increases battery consumption by 1%.
The potential impact of tires used on EVs is surprisingly high. The wrong kind of tire can impact battery consumption and increase noise, but this also works the other way around. For instance, ENSO Tyres can extend driving range, going up to 11.5% in the most drastic scenarios.
EVs consume around 1% of the battery per day in idle mode to power circuit boards and other components. If your vehicle consumes more than this, it is recommended to check features that might be draining your battery while in idle mode.
Another question we often get is: how often do electric car batteries need replacing?
Considering the estimated 1,500 – 2,000 cycles or 100,000 – 200,000 miles range, an EV battery can last for 15 to 20 years before replacing.
Figure 1: EV Battery Degradation Chart – Electrek
While many EV drivers wonder how long does an electric car battery charge last, few of them ask why? The main reason an EV battery needs replacement is that it has most likely degraded beyond 80% of its capacity.
According to researchers at Recurrent, EV batteries lose around 5% to 10% of their capacity after 50,000 miles or a little more. This means batteries degrade 5 – 10% after the first five years, Figure 1 shows a battery degradation rate (in km) for your better understanding.
You already know how long does a battery last in an electric car, but what happens after its life has ended? The good news is that EV batteries have a second life and then they are recycled to be born again.
EV batteries hold around 80% of their capacity when they need to be replaced. After being dismounted from the EV they are salvaged and repurposed for stationary and less demanding applications. Some smart home battery manufacturers use these types of batteries for their storage systems. After their second life ends, EV batteries are taking to be recycled.
Now you know practically everything about how long do batteries last in electric vehicles and what happens after they are replaced, but do you know how to increase the life of your battery? In this section we give you some important tips to achieve this:
Before charging an EV battery at night, you should check the State of Charge (SOC) and consider your driving needs for the next day. Charging an EV battery heats the whole thing and puts stress on it. Waiting for some time between charges if you drive short distances can be a great charging practice, we recommend waiting until a 20% SOC before recharging the battery.
Completely depleting or fully charging your EV battery is a bad charging practice. Some experts like battery researcher Qichao Hu consider that using a SOC between 10% – 90% is ideal, while researchers from Michigan stay more on the safe side and recommend a SOC range of 30% – 80%. You could adopt each of those, but we recommend using a SOC range between 20% – 80% per charge to be on the safe side.
When you use your EV daily you can go out one day on a full charge and use the remaining capacity for the rest of the week depending on your driving needs, but what happens if you do not use your EV every day? According to Tesla, EV batteries feature a self-discharge rate of 1% per day, but this is for new batteries, older batteries may self-discharge at a faster rate of up to 5%. Monitoring your EV battery SOC periodically (even if you do not use it) to account for self-discharging is a good practice.
When figuring out how long does an electric car last on one charge, you should consider storing, charging, and operating temperatures. Lithium-Ion EV batteries work perfectly in a temperature range of 77ºF up to 104ºF. In this temperature range, EVs charge as expected, feature low self-discharge rates and deliver the ideal driving range on one charge, but this is not the case for extreme temperatures.
EVs will self-discharge at low temperatures and take longer to charge. A considerable self-discharge begins at 65ºF, but the real battery drainage happens when batteries are exposed to 50ºF or lower temperatures. Temperatures should also be kept below 104ºF since higher temperatures can be harmful to the battery, operating at 122ºF or higher temperatures will most likely impact the lifespan of the battery.
For those who want to know how to extend the lifespan of the battery, rapid charging is something you ought to reduce as soon as possible. EV manufacturers like Kia and Tesla advise against this constant practice, charging an EV with DC Fast Chargers (DCFC) can reduce the overall battery capacity of the EV and accelerate its degradation.

Figure 3: EV battery second life
After the battery life expectancy for electric cars has reached its end, it is time for the batteries’ second life to start. Here we explain how EV batteries are reused and recycled afterward.
There will be around 85 million EVs worldwide by 2030, which is why finding a second life for the EV battery that can only retain 80% of its capacity can help the environment and the economy. Repurposed batteries or EV Second Life Batteries (SLB) can be used as stationary batteries for home battery storage systems, extending the lifespan of the battery by 4 or even 16 years more.
Most EVs with an SLB will be recycled by the end of that second life. Some EV Lithium-Ion batteries may not be as lucky and have to be recycled after they reach the end of their life for EV applications. Recycling EV batteries reduces waste by reusing valuable materials within EV batteries that can be used to manufacture new Lithium-Ion batteries or for many other applications.
Definitely, EV batteries can be replaced but they do not come cheap. The cost to replace the battery of an EV can go as high as $20,000. This is why we recommend planning for it and creating a budget considering the average lifespan of your EV. However, keep in mind that your battery will not probably need replacement until 20 years after you purchase the vehicle.

CyberSwitching EV Charger on Pedestal
CyberSwitching Dual EV Charging Station



