
Home / EV Charging News / Install A Home Charging Station for Your Electric Car
If you will be acquiring an Electric Vehicle (EV), you should be learning about EV charging stations, especially home EV charging stations. Many EV drivers charge their vehicles in public charging stations, but this requires more money and takes more of your time than charging at home.
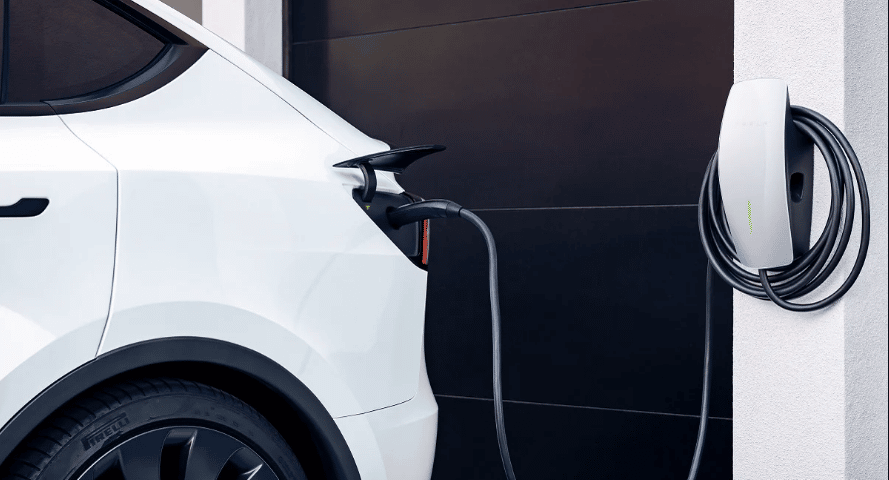

Figure 1: EV Connected to an EVSE
If you want to learn more about home EV charging stations and the EV home charger installation process, this article is for you. Here we explain the basics for home EV charging stations, the installation process, the steps previous to the installation, and more.
Traditional Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) vehicles require filling up the gas tank at gas stations. EVs instead have batteries that are charged at public or home EV charging stations.
A home EV charging station is an electrical device that takes power from the grid or an alternative energy source to charge the EV battery. Most home charging stations deliver AC power to the vehicle that is converted into DC at the on-board EV charger, this DC energy is used to directly charge the EV battery.
For the installation of a home EV charger, we recommend a Level 2 EV charger, since it features a power rate of 3 kW up to 12 kW, taking 3 to 13 hours to charge a 40 kWh EV battery. Level 1 EV charging stations deliver only 1 kW to the EV battery and takes 40 hours to charge the same battery.
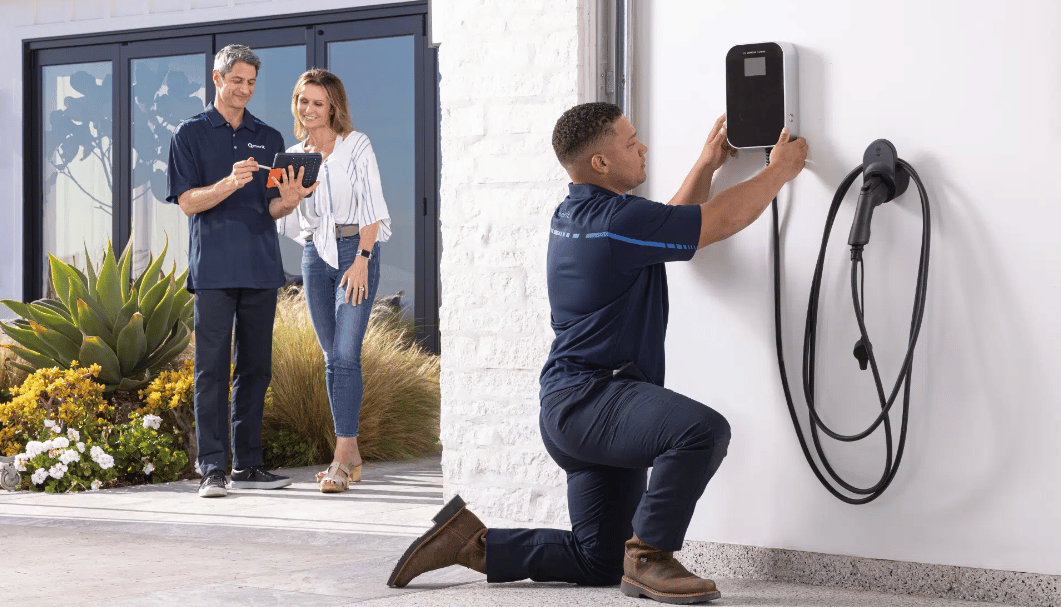

Figure 2: Home EV Charger Installation
Installing a home charging station is a relatively easy task, although it should be performed by a certified electrician. Level 1 EV chargers are usually plug-and-play chargers that use pre-existing circuits, while Level 2 EV chargers require a dedicated circuit with adequate wiring and a NEMA 14-30, 14-50, 10-30, 10-50, or 6-50 outlet, depending on the current demanded by the device. The circuit will require adequate electrical protection devices and proper cable sizing according to the National Electrical Code standards.
After the circuit for the EV home charger installation is installed, the device should be fixed by either a wall-mounted or a pedestal-mounted installation (although for residential cases it is more commonly wall-mounted). The last step for the car home charger installation is plugging the device and configuring the equipment if necessary. After that, you can charge your vehicle.
If you buy a new electric car, you need to prepare your home for it by installing a level 2 charger that can charge your vehicle overnight for a cheap cost. The charger should usually be located close to the service panel, and you should be able to park the car with the charging port facing the EV charger. The length of an EV charging wire goes from 16 to 25 ft., so you need to plan considering all the factors.
Electrical parameters at the service panel of the home should also be considered. A Level 2 EV charging station requires a split-phase electrical connection, available circuit slots in the service panel, and an available electrical capacity to fit the charger with a power rate going from 3 kW up to 12 kW.
Finally, another important preparation step for the home car charging installation is talking with your electrical company. You will be placing a considerable load and your utility should be aware of it. Besides, some utilities have Time-of-Use rates and other incentives that can save you money, these incentives are granted to EV owners installing home electric car charging stations.

Figure 3: EV Charging Status
It is important to be able to estimate the charging time for any particular EV. This is usually determined considering three factors: the power rate of the home EV charger, the power rate of the on-board EV charger, and battery capacity.
The power rate for an EV charger limits the maximum power that the charger can deliver to the vehicle. The on-board EV charger instead, limits the maximum current that the vehicle can efficiently handle. Finally, the battery capacity determines how much energy will be demanded by the vehicle until it is fully charged.
The following table illustrates the charging time for some popular vehicles in the U.S. using a 7.7 kW and a 9.6 kW home EV charger:
| EV Parameters | Charging time | |||
| EV Model | Battery capacity | On-board EV charger | 7.7 kW Charger | 9.6 kW Charger |
| Tesla Model Y | 60 kWh | 11 kW AC |
7 hours and 45 minutes (@ 7.7 kW) |
6 hours and 15 minutes (@ 9.6 kW) |
| Ford Mustang Mach-E | 98.7 kWh | 11 kW AC |
12 hours and 50 minutes (@ 7.7 kW) |
10 hours and 16 minutes (@ 9.6 kW) |
| Tesla Model S | 100 kWh | 16.5 kW AC |
13 hours (@ 7.7 kW) |
10 hours and 25 minutes (@ 12 kW) |
Table 1: Charging time for popular EV Models using 7 kW & 19 kW EV chargers
In this case, none of the chargers delivers more than the 11 kW or 16.5 kW that the on-board EV chargers can handle. If you use an AC charger featuring a power rate superior to that of the on-board EV charger, the top power delivered to the vehicle will that that of the on-board EV charger.
Installing a home car charger results in lower charging costs compared to public EV charging. To estimate the cost to charge an EV at home, you need to consider the cost of electricity. Calculating the estimated cost for a charging session requires you to multiply the capacity of the battery by the price for the kWh in your state, like this:
For instance, electricity costs 25.7 cents per kWh in some Californian cities, fully charging a Tesla Model Y costs around $15.42, while charging the Mustang and Model S costs around $25.7. Utilities with TOU rates can provide better rates during off-peak hours, making EV charging even cheaper.
Figure 4: EV Charger Installation
To simplify the steps required to install an electric car charger, we have summarized the most important ones in an easy-to-understand format. These are the following:
First, you have to determine and locate if there is a 240V outlet available at your home. This allows you to know if your home has a split-phase electrical connection, in some cases, you might even be able to use that circuit to install a car charging station at your home if there are no other loads connected. You should also assess the available capacity of the service panel at your home.
After learning about the electrical connection at your home and the available capacity of the service panel, you can buy a home EV charger. You can either match the specifications for the EV charger to the available electrical capacity at your home or you can upgrade your service panel to install a charger with a high power rate.
You can install an EV charging station by using the pre-existing electrical connection at your home. If there is no spare way available in the panelboard, or if the panelboard does not have enough electrical capacity left to accommodate the charger, then you will have to hire a certified electrician to set up the circuit for the car charger home installation and probably perform a main panel upgrade.
Some utilities provide excellent electricity plans for EV owners looking to charge their vehicles at home. Contact your utility and ask about available TOU plans to take advantage of lower tariffs during off-peak hours, charging your vehicle for a lower cost.
Finally, you should look into available incentives for EV owners installing an electric car charging point in your state. Many states have rebates and tax credits available that can reduce the overall cost of the installation for an EV charger.
For instance, utilities in California like Turlock Irrigation District and Truckee Donner Public Utility District offer $300 incentives for customers installing a car charging point. Others offer higher incentives, like Alameda Municipal Power offering $800 and Anaheim Public Utilities offering up to $3,000 for installing a networked level 2 charger.
